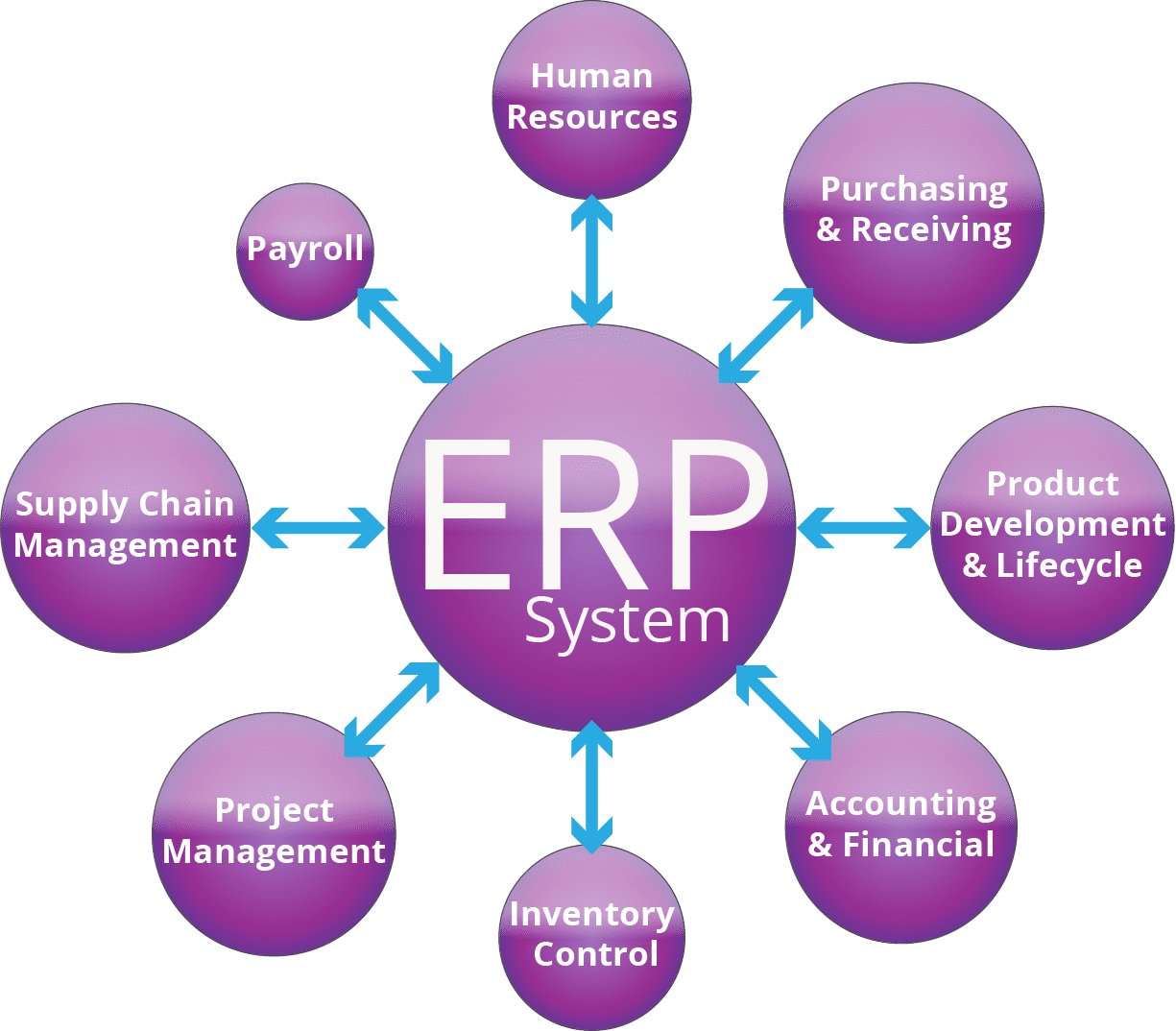
Welcome to our guide on essential ERP system requirements checklist! Whether you are considering implementing a new ERP system or looking to upgrade your current one, having a thorough understanding of the key requirements is crucial for the success of your project. In this article, we will discuss the important factors to consider when selecting an ERP system that best fits your organization’s needs and objectives.
Functional Requirements
Functional requirements are the key components that determine the core capabilities of an ERP system. These requirements directly relate to the specific functions and features that the system must perform to meet the needs of the organization. In order to ensure that the ERP system operates effectively and efficiently, it must have the following functional requirements:
1. System Integration: One of the primary functional requirements of an ERP system is its ability to seamlessly integrate with other systems within the organization. This integration should allow for the smooth flow of data and information between different departments and business processes. For example, the ERP system should be able to integrate with the organization’s financial systems, supply chain management software, and customer relationship management tools. This ensures that all relevant information is accessible in one centralized location, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors.
2. Customization: Another important functional requirement is the ability to customize the ERP system to meet the specific needs of the organization. This includes the ability to configure workflows, reports, and dashboards to reflect the unique processes and operations of the business. Customization also allows for the addition of new modules or features as the organization grows and evolves. A flexible and customizable ERP system ensures that it can adapt to changing business requirements and stay relevant in a dynamic environment.
3. Scalability: A scalable ERP system is crucial for organizations that plan to expand or grow their operations in the future. The system should be capable of handling an increase in users, transactions, and data volumes without compromising performance or stability. Scalability also allows the organization to add new functionalities or modules to the ERP system as needed, ensuring that it can support the business’s evolving needs and objectives.
4. Mobile Access: In today’s digital age, the ability to access the ERP system from any device, anywhere, and at any time is essential. Mobile access is a key functional requirement that enables users to stay connected and productive while on the go. Whether it’s checking inventory levels, approving purchase orders, or reviewing financial reports, mobile access ensures that employees have the information they need at their fingertips, improving decision-making and overall efficiency.
5. Security: Protecting sensitive data and information is a top priority for any organization, and the ERP system must have robust security features to prevent unauthorized access and safeguard against cyber threats. Security is a critical functional requirement that encompasses features such as user authentication, data encryption, role-based access controls, and audit trails. By implementing stringent security measures, the organization can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of its data within the ERP system.
In conclusion, functional requirements play a vital role in determining the effectiveness and success of an ERP system. By ensuring that the system meets the key functional requirements outlined above, organizations can leverage the full potential of their ERP solution and drive business growth and innovation.
Technical Requirements
When considering the technical requirements for an ERP system, it is important to ensure that the software is compatible with your existing hardware and network infrastructure. This includes assessing whether the ERP system can run on your operating system, server specifications, and database management system. It is also crucial to check if the ERP system can integrate with other software applications that are already in use within your organization.
In addition to compatibility, performance is another key technical requirement to consider. The ERP system should be able to handle the volume of data and transactions that your organization processes on a daily basis. This means ensuring that the system has enough processing power, memory, and storage capacity to support your operations. It is also important to consider scalability, as the ERP system should be able to grow with your business and accommodate future expansion.
Security is another critical technical requirement for an ERP system. With sensitive business data and confidential information stored within the system, it is essential to have robust security measures in place to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats. This includes encryption, user authentication, role-based access control, and regular security updates and patches to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Another important technical requirement to consider is data management. The ERP system should have the capability to efficiently capture, store, retrieve, and manipulate data from various sources across the organization. This includes data migration tools to transfer existing data into the new system, data cleansing and validation processes to ensure data accuracy and consistency, and data analytics and reporting capabilities to derive actionable insights from the data.
Integration is also a key technical requirement for an ERP system. The system should be able to seamlessly connect with other systems and applications within your organization, such as CRM, HR, accounting, and supply chain management software. This enables real-time data sharing, streamlined business processes, and improved collaboration across departments. Integration also extends to external systems, such as vendors, customers, and partners, to facilitate smoother communication and transactions.
Security Requirements
When it comes to implementing an ERP system, security requirements are vital to ensure that your company’s sensitive data is protected from potential threats. Here are some key security requirements that should be included in your ERP system checklist:
1. User Authentication: One of the first steps in securing your ERP system is implementing robust user authentication protocols. This includes requiring strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular password updates to prevent unauthorized access to the system. Additionally, user roles and permissions should be clearly defined to limit access to sensitive information based on job responsibilities.
2. Data Encryption: Another critical security requirement is data encryption. All data transmitted within the ERP system should be encrypted to prevent interception by hackers. This includes data in transit, at rest, and in use. Encryption ensures that even if a data breach were to occur, the stolen information would be unreadable without the encryption key.
3. Regular Security Audits: In addition to implementing security measures, it is essential to conduct regular security audits to identify and address any vulnerabilities in the system. This involves performing penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and compliance audits to ensure that the ERP system meets industry standards and regulatory requirements. By identifying weaknesses in the system proactively, you can take steps to strengthen security and prevent potential security breaches.
4. Secure Integration: If your ERP system integrates with other software applications or third-party systems, it is crucial to ensure that these integrations are secure. This includes encrypting communication between systems, implementing secure APIs, and regularly updating integration points to address any security vulnerabilities that may arise. Secure integrations help prevent unauthorized access to your ERP system through interconnected systems.
5. Disaster Recovery and Backup: Lastly, a key security requirement for an ERP system is a robust disaster recovery and backup plan. In the event of a security breach, natural disaster, or system failure, having a comprehensive plan in place to restore data and functionality is essential. Regularly backing up data and testing disaster recovery procedures helps ensure the continuity of business operations in the face of unforeseen events.
Overall, incorporating these security requirements into your ERP system checklist will help mitigate potential security risks and protect your company’s sensitive data. By prioritizing security measures and continuously monitoring the system for vulnerabilities, you can safeguard your ERP system against threats and maintain the integrity of your business operations.
Integration Requirements
Integration requirements are crucial for an ERP system to effectively communicate with other software applications used by the organization. When considering integration requirements, it is important to assess the following factors:
1. Compatibility with existing systems: The ERP system should be able to seamlessly integrate with the organization’s existing software applications such as CRM systems, human resource management systems, and accounting software. This will ensure that data can be easily shared between different systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors.
2. Flexibility for future integrations: In addition to integrating with current systems, the ERP system should have the flexibility to accommodate future integrations with new software applications that the organization may adopt. This will allow the organization to scale and adapt its technology infrastructure as needed without having to overhaul the entire ERP system.
3. APIs and data connectors: The ERP system should have robust APIs (application programming interfaces) and data connectors that enable seamless integration with third-party software applications. APIs are essential for enabling communication between different systems and transferring data securely. Data connectors facilitate the flow of data between the ERP system and other applications, ensuring that information is synchronized in real-time.
4. Data migration capabilities: One of the key aspects of integration requirements is the ERP system’s ability to migrate data from existing systems into the new system. Data migration can be a complex process, as it involves transferring large volumes of data without compromising data integrity. The ERP system should have built-in tools and processes for data migration, including data cleansing, data mapping, and data validation. Additionally, the system should be able to handle data migration in batches to minimize downtime and disruptions to the organization’s operations.
5. Real-time data synchronization: Real-time data synchronization is essential for ensuring that data is up-to-date and accurate across all integrated systems. The ERP system should be able to synchronize data in real-time with other applications, enabling users to access the most current information at all times. This is particularly important for organizations that rely on real-time data for decision-making and operational efficiency.
By considering these integration requirements, organizations can ensure that their ERP system is fully integrated with their existing software applications and can accommodate future integrations as needed. This will streamline processes, improve data accuracy, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Customization Requirements
Customization requirements are essential when considering an ERP system for your business. These requirements involve the ability to modify or personalize the system to meet your specific business needs. Here are some important customization requirements to consider:
1. User Interface Customization: The ERP system should allow for easy customization of the user interface to match the branding and visual identity of your business. This includes the ability to change colors, logos, and layouts to create a seamless user experience for your employees.
2. Workflow Customization: Every business has unique workflows and processes that are crucial for operations. The ERP system should provide flexibility in customizing workflows to align with your specific business processes. This includes the ability to automate tasks, set up approval hierarchies, and customize data entry forms.
3. Reporting Customization: Reporting is an essential function of an ERP system, as it provides valuable insights into business performance. The system should offer customizable reporting tools that allow you to create personalized reports tailored to your business needs. This includes the ability to manipulate data, create custom dashboards, and schedule automatic report generation.
4. Integration Customization: Integration with other software systems is often necessary for seamless operations. The ERP system should support easy integration with other business applications, such as accounting software, CRM systems, and e-commerce platforms. Customization requirements in this area involve the ability to tailor integrations to your specific requirements, ensuring smooth data flow between systems.
5. Module Customization: One of the key advantages of an ERP system is the availability of different modules that cater to various business functions, such as finance, inventory management, and human resources. Customization requirements for modules involve the ability to customize and configure each module according to your specific needs. This includes adding or removing features, setting up specific workflows, and integrating with third-party tools.
Overall, customization requirements are crucial for ensuring that the ERP system aligns with your business processes and goals. By carefully considering these requirements and selecting a system that offers the flexibility to customize various aspects, you can maximize the benefits of the ERP system for your business.
Originally posted 2024-03-01 02:21:57.